Revolution in Medical Education: How the Virtual Dissection Table is Transforming the Approach to Anatomy Education

The field of medical education is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by advances in technology. One of the most profound changes has been the introduction of virtual dissection tables, which are rapidly replacing traditional methods of teaching anatomy. These tables provide a unique, interactive platform for students to explore the human body in ways that were previously impossible with conventional cadaver dissection. In this article, we will explore how virtual technologies are revolutionizing the study of anatomy, comparing their advantages and disadvantages, and highlighting successful implementations in medical schools around the world. A special focus will be given to the Pirogov Interactive Anatomical Table, a prominent example of this technology from Russia.
The Shift from Traditional to Virtual Dissection
Traditionally, anatomy education has relied heavily on the dissection of cadavers. This method, while effective, comes with several limitations, including the availability of cadavers, ethical considerations, and the complexity of maintaining and storing specimens. The introduction of virtual dissection tables addresses many of these challenges, offering a modern alternative that aligns with the needs of today’s educational environment.
Advantages of Virtual Dissection Tables:
- Accessibility and Availability: Virtual dissection tables are available at any time and do not require the logistical arrangements necessary for cadaveric dissection. This allows for more flexible scheduling and the ability for students to learn at their own pace.
- Enhanced Visualization: Virtual tables provide highly detailed 3D models of the human body, which can be rotated, zoomed, and dissected in various planes. This allows students to visualize anatomical structures in ways that are not possible with traditional dissection, improving their understanding of complex spatial relationships.
- Interactive Learning: These tables offer interactive features that engage students actively in the learning process. They can perform virtual dissections, take quizzes, and explore various layers of anatomy, which promotes a deeper and more retained understanding of the material.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Over time, virtual dissection tables can be more cost-effective than maintaining a cadaver lab. They eliminate the recurring costs associated with acquiring and preparing cadavers and reduce the need for specialized storage facilities.
- Ethical Considerations: The use of virtual dissection avoids the ethical concerns associated with the use of human remains in education, making it a more widely acceptable option across different cultures and institutions.
Disadvantages and Challenges:
- Initial Cost: The upfront cost of acquiring a virtual dissection table can be high, which might be a barrier for some institutions, especially in resource-limited settings.
- Lack of Tactile Experience: One of the significant limitations of virtual dissection is the lack of tactile feedback. The physical manipulation of tissues and organs, which is crucial in traditional dissection, cannot be replicated digitally, potentially limiting the development of certain hands-on skills.
- Dependence on Technology: Virtual dissection tables require a stable technological infrastructure, including reliable power supplies and technical support. Any technical issues or software glitches can disrupt the learning process.
- Learning Curve: Both students and instructors may face a learning curve when adapting to the new technology. Proper training and acclimatization are necessary to fully leverage the potential of virtual dissection tables.
The Pirogov Interactive Anatomical Table
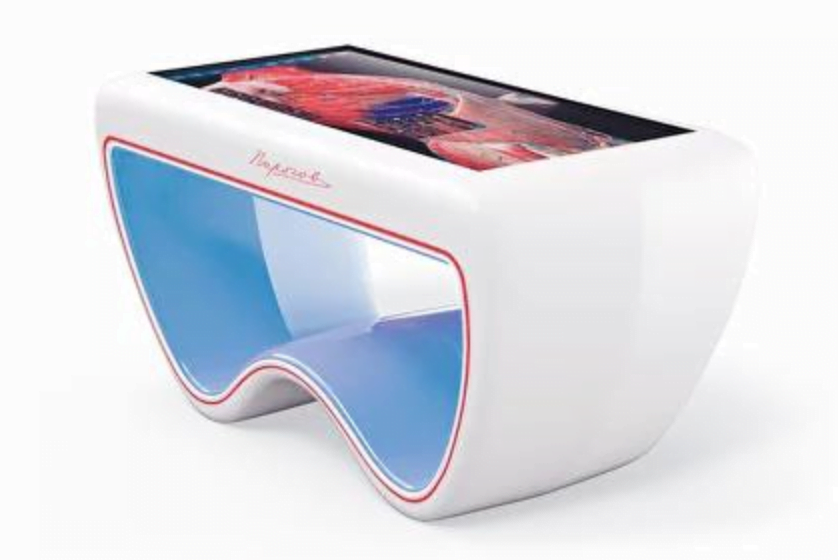

The Pirogov Interactive Anatomical Table is a cutting-edge virtual dissection table developed in Russia, which exemplifies the integration of modern technology with traditional medical education. This table offers a sophisticated platform that combines high-precision anatomical models with extensive educational features tailored to meet the needs of students and educators alike.
Key Features of the Pirogov Table:
- Precision and Detail: The Pirogov Table allows users to explore virtual human body models with a high degree of detail. All anatomical structures are presented with maximum accuracy, enabling the study of various levels—from general views to specific organs and tissues.
- Virtual Dissection: One of the table’s key functions is the ability to perform virtual dissections. Students can “cut” the body in various planes, examine internal organs, and understand their spatial relationships, making the learning process highly interactive and visually comprehensible.
- Multimodal Display: The Pirogov Table supports different display modes, including X-rays, CT, and MRI scans. This integration allows students to connect anatomical studies with radiology and other related disciplines, providing a comprehensive learning experience.
- Educational Modules and Testing: The table includes educational modules with theoretical materials, tests, and interactive assignments. This helps students not only acquire knowledge but also assess their understanding during the learning process.
- Mobile Application: The Pirogov Table is complemented by a mobile application designed for both teachers and students. This app extends the capabilities of the table beyond the classroom, offering access to anatomical models, quizzes, and educational resources anytime, anywhere. The app also allows teachers to create personalized learning paths and monitor student progress remotely, making it a valuable tool for both in-class and distance learning.
Successful Implementations in Medical Schools
Several medical schools around the world have successfully integrated virtual dissection tables into their curricula, demonstrating the effectiveness of this technology in enhancing anatomy education.
Case Study 1: Stanford University, USA
Stanford University is at the forefront of integrating technology into medical education. The university has adopted virtual dissection tables as a core part of its anatomy curriculum. These tables are used not only for basic anatomical education but also in advanced surgical training programs. Students have reported a greater understanding of complex anatomical structures and better preparation for clinical rotations due to the detailed and interactive nature of the virtual dissections.
Case Study 2: Sechenov University, Russia
Sechenov University in Moscow is another example of successful implementation. The university uses the Pirogov Interactive Anatomical Table to enhance the learning experience for its medical students. The integration of this technology has allowed students to explore human anatomy in unprecedented detail, leading to a deeper understanding of anatomical relationships and improved performance in practical exams.
Case Study 3: Manipal Academy of Higher Education, India
In India, the Manipal Academy of Higher Education has incorporated virtual dissection tables into its medical programs. This has significantly improved access to anatomical learning resources for a large number of students. The ability to study detailed anatomical models at any time has been particularly beneficial in overcoming the limitations of traditional cadaveric dissection, especially in a country with a large student population and limited access to cadavers.
Global Availability
The Pirogov Interactive Anatomical Table is not only used in Russia but is also available for order in several countries around the world. Educational institutions in India, Vietnam, Thailand, the Philippines, Malaysia, Saudi Arabia, Belize, Sint Maarten, Türkiye, Egypt, Tunisia, Pakistan, and Algeria can now access this advanced educational tool. This global availability underscores the Pirogov Table’s reputation as a versatile and effective tool for anatomy education, adaptable to different educational environments and cultural contexts.
Conclusion
The introduction of virtual dissection tables, such as the Pirogov Interactive Anatomical Table, marks a revolutionary shift in the way anatomy is taught in medical schools. While they offer numerous advantages, including enhanced accessibility, interactive learning, and cost-effectiveness, there are also challenges to be addressed, such as the lack of tactile experience and the high initial cost. However, the successful implementation of these tables in institutions around the world demonstrates their potential to significantly improve the quality of medical education. As technology continues to evolve, it is likely that virtual dissection tables will become an increasingly integral part of anatomy education, helping to prepare the next generation of healthcare professionals with the skills and knowledge they need to succeed.
Related Articles:-
- How to Choose the Right Node.js Development Company
- What Is Cloud Computing? What Are The Cloud Computing Types?
- Sustainable Technology: All That You Need to Know
